Back pain is a common problem that affects people of all ages. It is estimated that about 80% of people will experience back pain at some point in their lives. Back pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
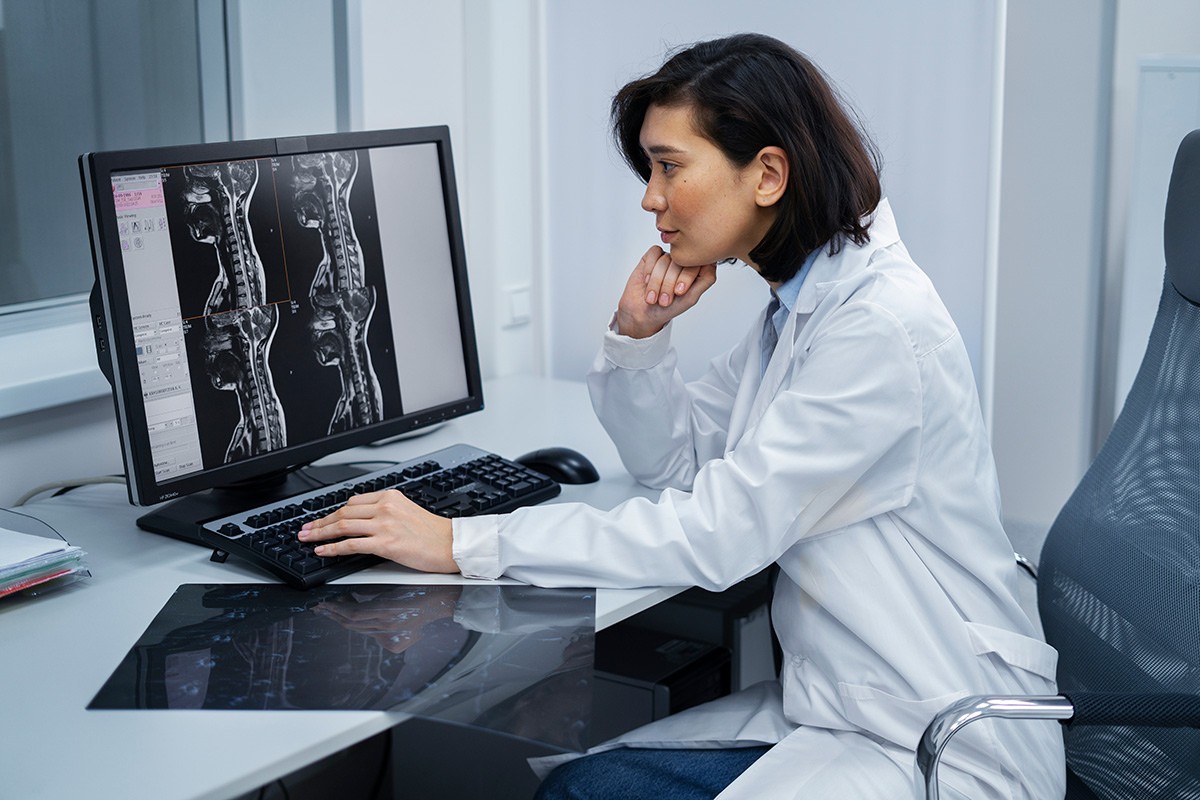
One of the main limitations of MRI scans for back pain is that they cannot always identify the cause of the pain. Back pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including muscle strain, ligament sprain, arthritis, spinal stenosis, and disc herniation. Not all of these conditions are visible on an MRI scan.
Another limitation of MRI scans is that they can be misinterpreted. The images from an MRI scan can be complex and difficult to interpret, even for experienced radiologists. In some cases, radiologists may misinterpret the images and miss an abnormality that is causing the patient's pain.
Even if an MRI scan does show an abnormality, it does not necessarily mean that the abnormality is causing the patient's pain. For example, a person may have a bulging disc on their MRI scan, but they may not be experiencing any pain.
So, what does this mean for people with back pain? It means that they should not rely on an MRI scan alone to diagnose the cause of their pain. Instead, they should work with their doctor to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that includes a thorough physical examination, medical history, and other diagnostic tests, as needed.

Here are some other limitations of MRI scans for back pain:
If you are experiencing back pain, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment plan. The doctor will work with you to find the best way to manage your pain and improve your function.
An MRI scan can be a useful tool for diagnosing back pain. However, it is important to remember that it is not always necessary and should only be used when other tests have not been able to provide a diagnosis. If you are considering an MRI scan for back pain, be sure to talk to your doctor first.